Building a Reliable Foundation for IT Operations | Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
By: Daniel N.
What is the CMDB?
Modern IT operations span a complex mix of physical infrastructure, virtual environments, cloud platforms, and deeply interconnected applications. On top of it, business is constantly changing. Whether things break or the business itself must evolve, adaption demands tweaking dozens of things at once. And that requires understanding the current state of the entire living system: how everything fits together, and what those relationships mean in terms of downstream impact in real-time. The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) answers these questions.
ServiceNow’s CMDB serves as the system of record for the technology that runs the business. It centralizes information about infrastructure, platforms, applications, and services, along with the relationships between them, across on-premises and cloud environments. With a trusted CMDB in place, IT teams gain visibility not only into what exists, but how components depend on one another, enabling faster troubleshooting, more accurate change-impact analysis, and better alignment between technology decisions and business priorities.
By consolidating configuration data and keeping it continuously updated, the CMDB becomes the foundation for operational excellence. It is not just an inventory; it is a real-time structural model of IT operations that reflects everything from individual servers to the business processes that run across it.
Building the CMDB
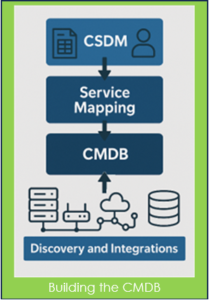 Building and maintaining a useful CMDB requires four capabilities working together, each with a clearly defined role. Discovery and integrations operate bottom-up, continuously identifying infrastructure by observing how systems exist and interconnect across on-premises and cloud environments. Service Mapping operates top-down, using defined application entry points to show how critical services run in the real world and how they depend on infrastructure. The Common Service Data Model (CSDM) provides guidance and defines what is worth modeling, establishing service boundaries, ownership, and governance so the CMDB focuses on the services that truly matter. Around and guarding the CMDB, the Identification and Reconciliation Engine (IRE) and CI Class Manager act as the normalization layer, ensuring that everything entering the CMDB is clean, consistent, and correctly classified.
Building and maintaining a useful CMDB requires four capabilities working together, each with a clearly defined role. Discovery and integrations operate bottom-up, continuously identifying infrastructure by observing how systems exist and interconnect across on-premises and cloud environments. Service Mapping operates top-down, using defined application entry points to show how critical services run in the real world and how they depend on infrastructure. The Common Service Data Model (CSDM) provides guidance and defines what is worth modeling, establishing service boundaries, ownership, and governance so the CMDB focuses on the services that truly matter. Around and guarding the CMDB, the Identification and Reconciliation Engine (IRE) and CI Class Manager act as the normalization layer, ensuring that everything entering the CMDB is clean, consistent, and correctly classified.
Discovery anchors the CMDB in physical and cloud reality. It is fully automated and intentionally opinionated: if something exists in the environment, Discovery finds it. Servers, virtual machines, containers, operating systems, databases, and core platforms are identified and kept current as the environment changes. ServiceNow balances accuracy with flexibility by supporting integrations to existing sources of truth, such as virtualization platforms, directory services, cloud providers, and other enterprise systems, while minimizing manual effort and technical debt. This creates a reliable, continuously refreshed baseline of what actually exists.
 As data flows into the CMDB from Discovery and integrations, IRE and the CI Class Manager ensure it is reconciled into a single, reliable model. Identification rules determine whether incoming data represents a new configuration item, an update to an existing one, or something that should be ignored. Class definitions, inheritance, rule ordering, and source trust rankings ensure disparate data arrives in a consistent form, preventing duplication, record sprawl, and conflicting representations of the same asset. This normalization step is critical, it allows multiple data sources to coexist without eroding trust in the CMDB.
As data flows into the CMDB from Discovery and integrations, IRE and the CI Class Manager ensure it is reconciled into a single, reliable model. Identification rules determine whether incoming data represents a new configuration item, an update to an existing one, or something that should be ignored. Class definitions, inheritance, rule ordering, and source trust rankings ensure disparate data arrives in a consistent form, preventing duplication, record sprawl, and conflicting representations of the same asset. This normalization step is critical, it allows multiple data sources to coexist without eroding trust in the CMDB.
Service Mapping builds on that foundation in the application layer. It does not attempt to infer every possible service or scan every process. Instead, it traces defined entry points, such as web endpoints, APIs, or message listeners, and follows live connections across application tiers to reveal real runtime behavior. Discovery establishes what is present; Service Mapping shows how those components work together to deliver functionality.
CSDM provides the strategic context that binds the model together. It defines which applications and services are worth modeling, who owns them, and which business services they support. This layer is intentionally manual, because only people can determine what matters to the business. If everything is treated as equally important, the model quickly loses value. CSDM ensures the CMDB reflects business priorities, not just technical complexity.
When these layers operate in concert, the CMDB evolves from a static inventory into a living model of the IT estate. Infrastructure reality is discovered, data is normalized and reconciled, application behavior is mapped, and business intent is applied. The result is a CMDB that remains accurate amid constant change and provides the clarity needed for confident, proactive decision-making, keeping IT operations aligned with both technical reality and strategic priorities.
CMDB Benefits
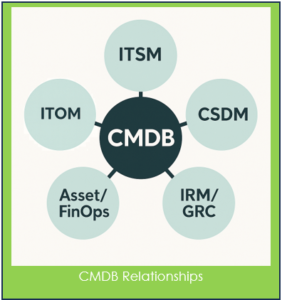
The CMDB connects ServiceNow’s operational, service, risk, and financial capabilities. By providing accurate, continuously updated configuration and relationship data, the CMDB enables each domain to operate with clarity, consistency, and context rather than in isolation.
This shared perspective allows every ServiceNow capability, from operations and monitoring to risk and finance, to work from the same understanding of how technology is built, owned, and interconnected.
IT Service Management (ITSM)
The CMDB provides the operational context that makes ITSM effective:
- Incident Management: Faster resolution through immediate visibility into affected CIs, ownership, and downstream service impact.
- Change Enablement: Safer change planning with accurate dependency and blast radius awareness.
- Problem Management: Root cause analysis driven by historical CI relationships and failure patterns.
- Request & Release Management: Automated, low-risk fulfillment and deployment tied to known services and infrastructure.
IT Operations Management (ITOM)
ITOM relies on the CMDB as its operational truth:
- Discovery & Service Mapping: Populate and enrich the CMDB with real infrastructure and application runtime behavior.
- Event Management & AIOps: Correlate alerts to the correct services and infrastructure to reduce noise and focus response.
- Observability: Provide service-aware monitoring aligned to actual dependencies rather than isolated metrics.
Service & Application Modeling (CSDM / Service Portfolio)
The CMDB enables a consistent service model across the enterprise:
- Business, Technical, and Application Services: Clearly defined, governed, and owned.
- Service Portfolio Management: Accurate representation of what services exist and what supports them.
- Impact & Dependency Views: Reliable service hierarchies grounded in operational reality.
Strategic Portfolio & Application Management (SPM / APM)
The CMDB informs planning and investment decisions:
- Application Rationalization: Understand application usage, dependencies, and risk.
- Project & Demand Planning: Assess impact and feasibility against real infrastructure and services.
- Technology Modernization: Identify candidates for modernization, consolidation, or retirement based on dependency data.
Risk, Governance, and Compliance (IRM / GRC)
The CMDB defines scope and context for risk management:
- Risk Identification: Understand which services and assets are in scope.
- Control Mapping: Link controls to actual systems and services.
- Audit & Compliance: Demonstrate traceability and accountability backed by real configuration data.
Asset, Software, and Financial Management (HAM / SAM / FinOps)
The CMDB provides lifecycle and cost clarity:
- Hardware Asset Management: Track assets in context of the services they support.
- Software Asset Management: Tie license usage and compliance to real installations and dependencies.
- Financial Visibility: Support service-level cost modeling and allocation based on actual infrastructure and usage.
Whether operational, financial, or risk-driven, the CMDB shares a consistent understanding of the environment and reduces duplication, prevents siloed decision-making, and ensures every process.
CMDB Tools
Keeping a CMDB accurate over time requires more than initial population; it requires continuous oversight, accountability, and the ability to correct issues as the environment changes. ServiceNow provides a set of dedicated CMDB administrative tools designed specifically to help CMDB owners actively govern data quality, detect degradation early, and maintain trust in the CMDB as systems, services, and ownership evolve. These tools enable teams to manage the CMDB as an operational system rather than a periodic cleanup exercise.
- CMDB Workbench: Acts as the operational control center for CMDB governance, bringing health metrics, remediation tasks, duplication management, and identification rules into a single workspace. It enables teams to proactively maintain the CMDB instead of responding to problems after data quality has already declined.
- CMDB Health Dashboard: Provides real-time visibility into CMDB data quality across completeness, correctness, and compliance. Health scores can be viewed by CI class, service, or ownership group, allowing teams to focus improvement efforts where accuracy matters most.
- Deduplication Engine: Identifies and safely resolves duplicate configuration items already present in the CMDB. It preserves relationships, references, and historical data, ensuring cleanliness and consistency as discovery and integrations continue to scale.
- Certification & Attestation: Introduce accountability into CMDB governance by requiring CI and service owners to periodically review and certify data accuracy. This ensures the CMDB remains trusted, auditable, and aligned as environments and responsibilities change.
Together, these tools provide the operational discipline needed to sustain a healthy CMDB in real time. They turn CMDB management from a reactive, manual effort into an intentional, repeatable practice, ensuring data remains accurate, ownership stays clear, and the CMDB continues to serve as a reliable foundation for IT operations and decision-making.
