Continual Improvement Management | IT Service Management
By: Jenise B.
What is Continual Improvement Management?
Continual Improvement is ‘the process of a business culture of on-going improvement’. Continual Improvement Management is an application that helps implement and find new improvement opportunities for services, people, processes, and function improvements across applications using prebuilt integrations like performance analytics. This unifies the improvement goals and progression throughout an organization. It can also align improvement plans to business strategy.
The Four Steps in implementing Continual Improvement Management into an organization culture is:
- To identify improvement opportunities.
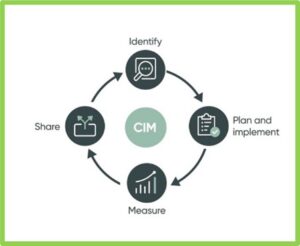
- Plan and implement the initiatives.
- Measure the impact by using Key Performance Indicator (KPIs)
- Share the value that was achieved.
What Problems Does Continual Improvement Management Address?
Organizations have many different reasons why Continual Improvement Management may work more effectively to achieve their goals for improved progression within their business plans. Some Reasons include:
- The organization has a Continual Improvement Plan but no tool to execute such CI initiatives on an end-to-end basis in an effective way.
- CIM helps with identifying the new implementation opportunities that are used within multiple tools to a more centralized place for the organization’s Improvement management Initiative.
- Many Improvement Plans are executed Reactively, Continual Improvement Management provides a more proactive approach.
- Other Management provides a difficult way to present outcome achieved from Continual Improvement.
Difference Between Demand/Project Management (PPM) and Continual Improvement Management
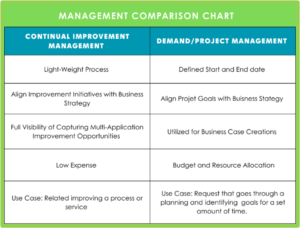 While Traditional Management like Demand and Project management can be integrated with Continual Improvement management, there are differences that helps decide which management approach works best for the process or goal for an organization’s business strategy.
While Traditional Management like Demand and Project management can be integrated with Continual Improvement management, there are differences that helps decide which management approach works best for the process or goal for an organization’s business strategy.
If the strategy involves defined start and end date, Budget Allocation and Business Case creation, it’s likely best fitted for a traditional management approach. If it’s low cost with a high purpose of improvement for a process or service, Continual Improvement Management would be the best fit for that business strategy. Continual Improvement management can work alongside Demand or Project Management, but it can also work independently from traditional management.
Workflow and Key Roles in CIM
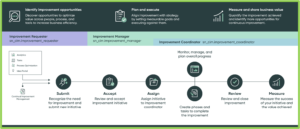
The typical workflow process involves a record being submitted by an Improvement Requester (sn_cim.improvement_requester) to identify the need of improvement and provide a new initiative to implement it. The Improvement manager (sn_cim.improvement_manager) can review and accept initiative. They will also be responsible for assigning the initiative to an Improvement Coordinator (sn_cim.improvement_coordinator). The improvement Coordinator is responsible for managing and creating an overall progress plan, through phases and tasks, that needs to be completed for the improvement. The Improvement Manger and Coordinator are both able to manage and plan the progress, review, and close the Improvement Initiative. Lastly, they are responsible for measuring the success of the initiative and the value achieved from the initiative.
CIM Workbench and Dashboard
Continual Improvement Workbench is used to plan and manage the improvements of the initiatives. Improvement manager and Improvement coordinator can use both Workbench and Dashboard. Workbench provides a graphical view to help adjust their business needs. Mangers use it to run planning meetings and to provide quick status updates to stakeholders.
The CIM Dashboard is used to view improvement reports. This shows reports and spotlight lists that can be filtered based on priority, state, process, and much more. If you have a report that needs more priority in viewing the improvement, Spotlight can help prioritize the list. Outcome analyses are used to view achieved outcomes within the last 6 months.
Sources from ServiceNow Documentation:
